I5904
Iberiotoxin, recombinant from Mesobuthus tamulus
≥98% (HPLC), recombinant, expressed in E. coli
Sinónimos:
IbTX
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C179H276N50O56S7
Peso molecular:
4248.86
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Productos recomendados
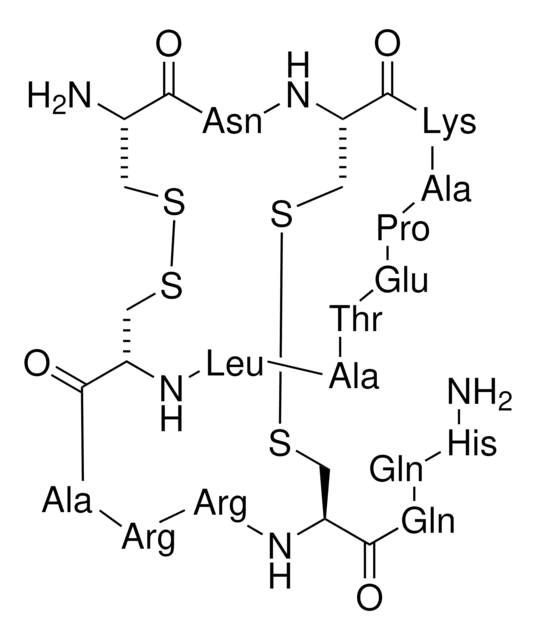
Amino Acid Sequence
Glp-Phe-Thr-Asp-Val-Asp-Cys-Ser-Val-Ser-Lys-Glu-Cys-Trp-Ser-Val-Cys-Lys-Asp-Leu-Phe-Gly-Val-Asp-Arg-Gly-Lys-Cys-Met-Gly-Lys-Lys-Cys-Arg-Cys-Tyr-Gln [Disulfide Bridges: 7−28; 13−33; 17−35]
Application
Iberiotoxin, recombinant from Mesobuthus tamulus has been used as an inhibitor of large-conductance calcium-activated K+ channels to study its effect on the NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor containing pyrin domain 3) inflammasome activation in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). It has also been used to block Ca2+- activated K+ channels to determine interleukin(IL)-1β in BMDCs following inflammasome activation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The single chain peptide iberiotoxin (IbTX) is a selective and reversible inhibitor of high-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (PK,Ca). It occurs naturally in the venom of the scorpion Buthus tamulus. IbTX also modulates the binding of charybdotoxin (CbTX) to smooth muscle sarcolemmal membranes in a non-competitive manner. IbTX is similar in size to CbTX and shares considerable sequence homology with CbTX. However, IbTX differs in its overall charge in having one fewer basic and four more acidic residues than CbTX.
Exhibits the same activity as the natural form of the toxin
Features and Benefits
This compound is featured on the Potassium Channels page of the Handbook of Receptor Classification and Signal Transduction. To browse other handbook pages, click here.
Preparation Note
Soluble in aqueous buffers. Stock solutions of 1 μM can be aliquoted and stored at -20 °C for up to 3 months.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 1 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 2 Dermal - Acute Tox. 2 Oral
Storage Class
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
The TWIK2 potassium efflux channel in macrophages mediates NLRP3 inflammasome-induced inflammation
Di A, et al.
Immunity, 49(1), 56-65 (2018)
Targeting TMEM176B Enhances Antitumor Immunity and Augments the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Blockers by Unleashing Inflammasome Activation
Segovia M, et al.
Cancer Cell, 35(5), 767-781 (2019)
Yan Li et al.
Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 9(11) (2020-11-19)
Opening of large conductance calcium-activated and voltage-dependent potassium (BKCa) channels hyperpolarizes plasma membranes of smooth muscle (SM) to cause vasodilation, underling a key mechanism for mediating uterine artery (UA) dilation in pregnancy. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has been recently identified as
Anke Di et al.
Immunity, 49(1), 56-65 (2018-07-01)
Potassium (K+) efflux across the plasma membrane is thought to be an essential mechanism for ATP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation, yet the identity of the efflux channel has remained elusive. Here we identified the two-pore domain K+ channel (K2P) TWIK2 as
Mercedes Segovia et al.
Cancer cell, 35(5), 767-781 (2019-05-16)
Although immune checkpoint blockers have yielded significant clinical benefits in patients with different malignancies, the efficacy of these therapies is still limited. Here, we show that disruption of transmembrane protein 176B (TMEM176B) contributes to CD8+ T cell-mediated tumor growth inhibition by
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico