F5542
Fibroblast Growth Factor-Acidic human
≥97% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
FGF-1, aFGF
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Fibroblast Growth Factor-Acidic human, FGF-Acidic, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, suitable for cell culture
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
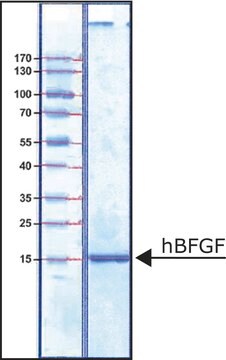
≥97% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
potency
0.287 ng/mL
quality
endotoxin tested
mol wt
15.5 kDa
packaging
pkg of 25 μg
General description
Fibroblast Growth Factor-Acidic (FGF1) belongs to the FGF family and comprises a nuclear export sequence (NES). FGF1 gene is mapped to human chromosome 5q31.3. FGF1 is highly expressed in the central and peripheral nervous system.
Application
Fibroblast Growth Factor-Acidic human has been used:
- as a component of growth factor cocktail for treating neural stem cell (NSC) transplants
- as a component of Human Neural Stem Cell (HNSC) proliferation medium for Neural Tissue Spheres (NTS) propagation
- as a growth factor component in fibrin matrix to support embryonic day 14 (E14) cells graft survival
Biochem/physiol Actions
Fibroblast Growth Factor-Acidic (FGF1) is a potent mitogenic agent associated with a variety of tissue origins including liver, vasculature, and skin. These include for a wide variety of mesoderm-derived cells including BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts, capillary and endocardial endothelial cells, myoblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells, mesothelial cells, glial and astroglial cells, and adrenal cortex. FGF1 participates in glucose homeostasis, adipose tissue remodeling and is a key transducer of the nuclear receptor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ). FGF1 is a neuronal cell neurotrophic factor and binds to most of the isoforms of the FGF receptor (FGFR) isoforms. Along with FGF2, FGF1 plays a key role in angiogenesis and favors blood vessel formation in chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. The FGF1 mutant R50E leads to suppression of its angiogenic potential making it a potential anti-angiogenesis agent.
Physical form
The product is lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20 mM Tris, 1 M NaCl, 5 mM DTT containing 50 μg of bovine serum albumin per 1 μg of cytokine.
Analysis Note
The proliferative activity is tested in culture using quiescent NR6R-3T3 fibroblasts.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Paul Lu et al.
Cell, 150(6), 1264-1273 (2012-09-18)
Neural stem cells (NSCs) expressing GFP were embedded into fibrin matrices containing growth factor cocktails and grafted to sites of severe spinal cord injury. Grafted cells differentiated into multiple cellular phenotypes, including neurons, which extended large numbers of axons over
T Yamashita et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 277(2), 494-498 (2000-10-18)
We isolated mouse cDNA encoding a novel FGF (251 amino acids). As this is the 23rd documented FGF, we termed it FGF-23. FGF-23 has a hydrophobic amino terminus ( approximately 24 amino acids), which is a typical signal sequence. As
Zhifeng Huang et al.
Cell reports, 20(7), 1717-1728 (2017-08-17)
The recent discovery of metabolic roles for fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) in glucose homeostasis has expanded the functions of this classically known mitogen. To dissect the molecular basis for this functional pleiotropy, we engineered an FGF1 partial agonist carrying triple
A Rizzino et al.
Cancer research, 48(15), 4266-4271 (1988-08-01)
The work described in this paper demonstrates that the cellular binding of transforming growth factor beta, epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor is reduced as cell density is increased. The reduction in transforming growth factor beta
Brian V Lien et al.
Experimental neurology, 314, 46-57 (2019-01-18)
Neural stem cells (NSCs) can differentiate into both neurons and glia after transplantation into spinal cord injury (SCI) sites. The neuronal component of stem cell grafts has the potential to form functional synaptic relays across the lesion site. The glial
Articles
Fibroblast growth factors in cell culture and various growth factors for your research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service